24th March 2020, Period 3, 9.30 to 10.20 am,Class XII, EG, Topic: Isometric Projection - 2
Isometric Projection - 2
Some basic Concepts.....contd.
1. What is a helping figure and why is it needed?
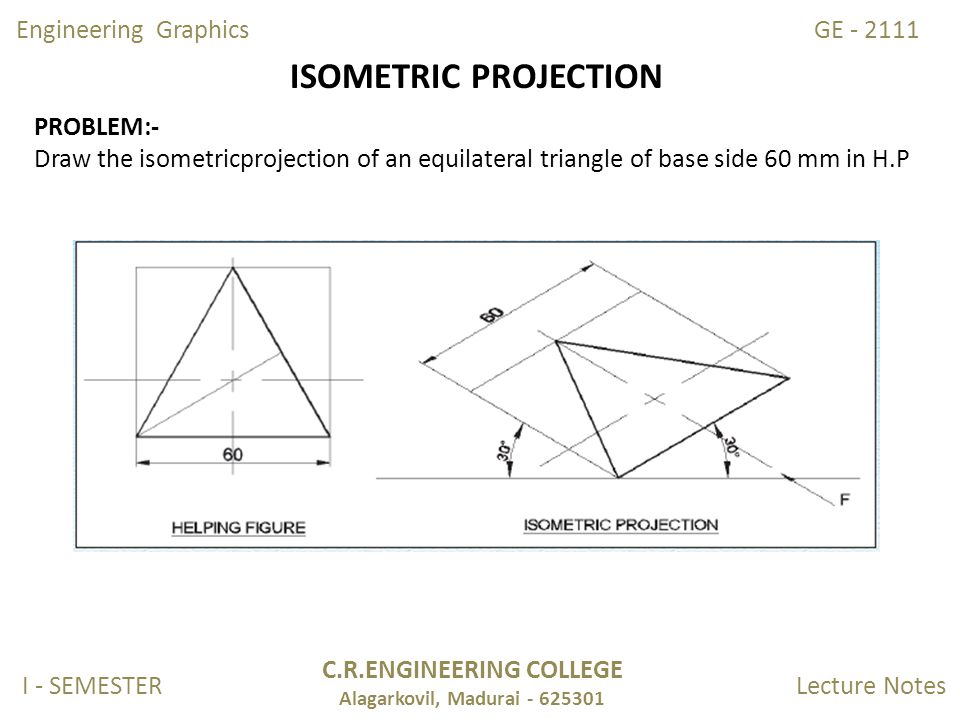
a). You have learnt yesterday that when an Isometric Projection of an object is drawn, its dimensions suffers a reduction of approx. 18.5%. An object may have both, isometric as well as non-isometric edges (lines). Therefore, to help us in drawing the isometric projection on non-isometric edges, we need the help of a 'helping figure'.
b). A square and a rectangle do not have non-isometric edges, therefore these shapes (figures) do not need a 'helping figure' to draw their Isometric Projections. However, triangle, pentagon and a hexagon have non-isometric edges, hence we need a helping figure to draw their Isometric Projections.
2. What is another good use of a helping figure?
We use a helping figure to mark the centre of the base (or face) through which the solid axis passes.
3. What are the essentials of an Isometric Projection?
a). Direction of viewing : Any Isometric Projection should have the direction of viewing. It is marked by a small line with an arrowhead.
b). Proper dimensioning: We should mark dimensioning lines in a proper manner, unlike in orthographic projection. The dimension lines are drawn parallel to the three axes.
c). Titles and Sub-titles: All projections, including Isometric Projections should mention the titles and subtiles (wherever necessary) that give the information about the object in question.
d). Proper lines: Axis, dimension
e). Hidden edges: of the object are not shown at all. No light lines and no dotted lines.
Exercise 2: Isometric Projection of planar figures
Instructions:a. Show direction of viewing, mark its centre and mention dimensions in all the above questions.
b. Solve these questions in your drawing file
c. Please take a picture of your answers (in one image) and post them in the EG Group.
Q 1. Draw the Isometric Projection of a pentagon of side 30 mm whose surface is parallel to the VP and one of its base edges parallel to the HP.
Q 2. Draw the Isometric Projection of a hexagon of side 40 mm whose surface is parallel to the HP and one of its base edges away from the observer parallel to the VP.
Q 3. Draw the Isometric Projection of a circle of diameter 50 mm whose surface is parallel to the VP.
Good Morning Students. Hope all are logged in for the class.
ReplyDeleteMorning sir
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
Delete